Delving into the realm of smart grid and energy-efficient solutions, this introductory paragraph aims to spark curiosity and provide a glimpse into the innovative technologies shaping the energy landscape. As we uncover the intricate details of smart grids and their impact on sustainability, a world of possibilities unfolds before us.
Moving forward, let's explore the components, benefits, challenges, and barriers associated with these cutting-edge solutions.
Overview of Smart Grid and Energy-Efficient Solutions
Smart grid technology revolutionizes the traditional energy sector by integrating advanced digital communication and automation to enhance efficiency and reliability.
Energy-efficient solutions play a crucial role in promoting sustainability by optimizing energy consumption, reducing waste, and minimizing environmental impact.
Comparison between Traditional Energy Systems and Smart Grid Technologies
Traditional energy systems rely on centralized power generation and distribution, resulting in inefficiencies and potential grid failures. In contrast, smart grid technologies enable decentralized energy production, real-time monitoring, and demand response mechanisms to improve overall system performance.
Components of Smart Grid Systems
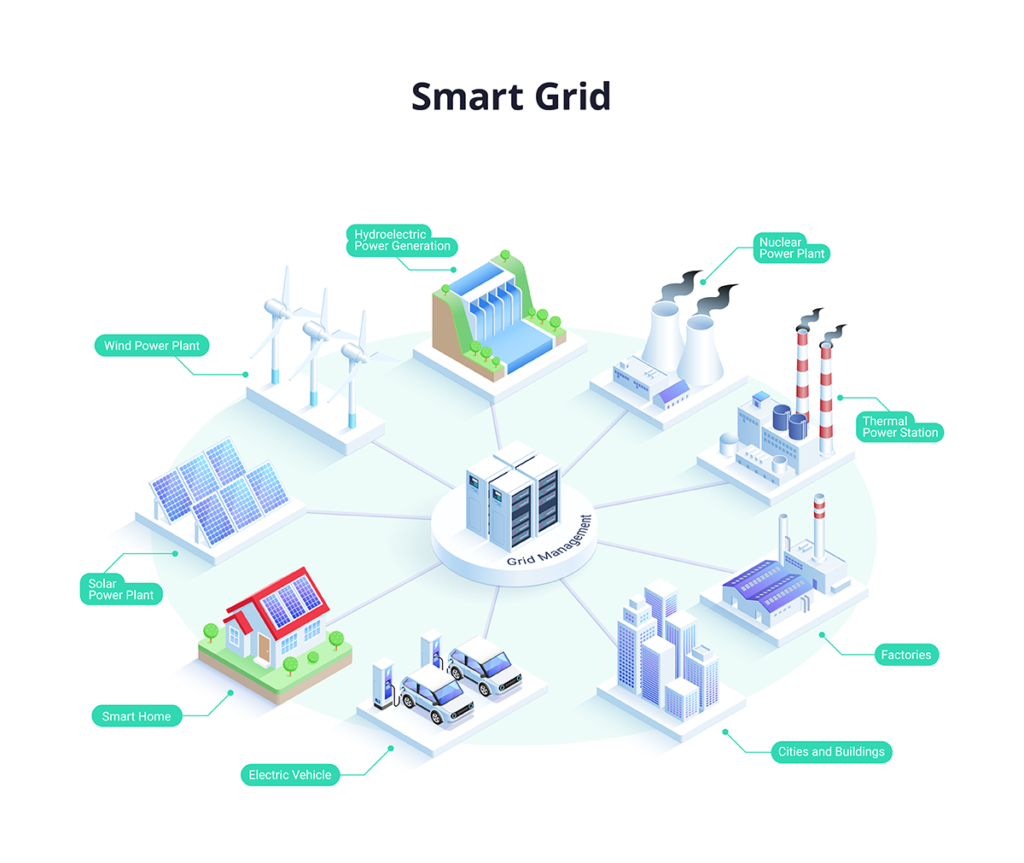
Smart grid systems consist of various key components that work together to improve efficiency, reliability, and sustainability in energy distribution.
Sensors
Sensors play a crucial role in smart grid systems by collecting real-time data on energy consumption, grid performance, and environmental conditions. These sensors enable utilities to make informed decisions and optimize grid operations.
Meters
Smart meters are essential components of smart grid systems as they provide detailed information on energy usage to both consumers and utility companies. By monitoring energy consumption patterns, smart meters help in promoting energy efficiency and reducing wastage.
Communication Networks
Communication networks are the backbone of smart grid systems, allowing seamless data exchange between various components. These networks enable remote monitoring, control, and automation of grid operations, leading to improved reliability and flexibility.
Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
Smart grid systems facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydro power. By leveraging advanced technologies and grid management strategies, renewable energy sources can be efficiently integrated into the grid, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions.
Energy Storage Devices
Energy storage devices play a critical role in optimizing smart grid operations by storing excess energy during off-peak hours and releasing it during times of high demand. This helps in balancing supply and demand, enhancing grid stability, and supporting the integration of intermittent renewable energy sources.
Benefits of Implementing Energy-Efficient Solutions
Energy-efficient solutions offer a wide range of benefits, not only to consumers but also to the environment. Let's explore some of the key advantages below.
Environmental Benefits
Implementing energy-efficient solutions helps in reducing the overall carbon footprint and mitigating the impact of climate change. By using less energy to perform the same tasks, these solutions contribute to lower greenhouse gas emissions, helping to preserve the environment for future generations.
Cost Savings for Consumers
Energy-efficient solutions can lead to significant cost savings for consumers in the long run. By using less energy, households and businesses can lower their utility bills, resulting in more money saved over time. Additionally, energy-efficient appliances and technologies often require less maintenance and have a longer lifespan, further reducing costs for consumers.
Reduction of Carbon Emissions
Energy-efficient technologies play a crucial role in reducing carbon emissions. By optimizing energy use and reducing waste, these solutions help in decreasing the amount of greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere. This not only benefits the environment but also contributes to global efforts in combating climate change.
Challenges and Barriers in Adopting Smart Grid Technologies
As promising as smart grid technologies are, their adoption is not without challenges and barriers that need to be addressed for successful implementation.
Regulatory Challenges in the Implementation of Smart Grid Systems
Regulatory challenges play a significant role in hindering the widespread adoption of smart grid systems. These challenges involve issues such as outdated regulations that do not accommodate new technologies, complex approval processes for grid upgrades, and the need for regulatory bodies to adapt to the rapidly evolving energy landscape.
Cybersecurity Concerns Related to Smart Grid Infrastructure
Cybersecurity is a critical concern when it comes to smart grid infrastructure. The interconnected nature of smart grid components makes them vulnerable to cyber attacks, which can have severe consequences on the reliability and security of the grid. Protecting against cyber threats requires robust security measures, continuous monitoring, and a proactive approach to cybersecurity.
Interoperability Issues Between Different Smart Grid Components
Interoperability between different smart grid components is essential for the seamless integration and functioning of the overall system. However, interoperability issues can arise due to the use of proprietary technologies, lack of standardized communication protocols, and compatibility issues between legacy systems and new smart grid devices.
Resolving these interoperability challenges is crucial for maximizing the effectiveness and efficiency of smart grid systems.
Last Word
In conclusion, the journey through smart grid and energy-efficient solutions has shed light on the transformative power of technology in the energy sector. From environmental benefits to cost savings, the future looks bright as we navigate the challenges and embrace the opportunities presented by these advancements.
FAQ Section
What are the key components of a smart grid system?
The key components include sensors, meters, and communication networks that enable efficient energy management.
How do energy-efficient solutions contribute to cost savings?
Energy-efficient solutions help reduce energy consumption, leading to lower utility bills for consumers.
What are the regulatory challenges in implementing smart grid systems?
Regulatory challenges often involve issues related to grid modernization, data privacy, and cybersecurity.
How do energy-efficient technologies impact carbon emissions?
Energy-efficient technologies help reduce carbon emissions by promoting sustainable energy practices.